Protecting Financial Transactions Against Malware
An analysis specific to Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
What is APT?
Long-term attacks by various cyber attackers and APT groups infiltrating critical telecom infrastructures and financial systems to cause significant damage.
Advanced Persistent Threat
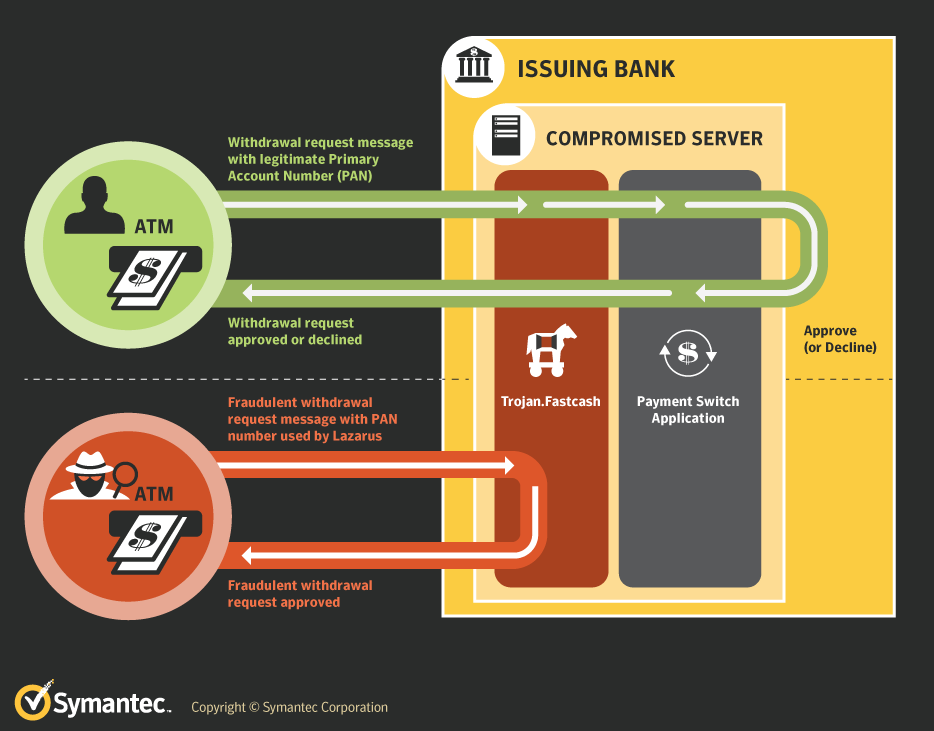
Example of APT: FastCash (Hidden Cobra)
Unauthorized cash withdrawals from ATMs through ISO 8583 protocol.
Developed by a group originating from East Asia.
Detected in 2018.
Believed to have been active since 2016.
Infects ATM switch as malware.
Approves incoming requests without authorization.
Example of APT: FastCash (Hidden Cobra)
Since 2018, it has started being detected by antivirus software.
Symantec bulletin: https://www.security.com/threat-intelligence/fastcash-lazarus-atm-malware
As of 15th October 2024, a new Linux variant of the FASTCash malware was discovered.
- North Korean threat actors
- Targets banking systems
- Steals interbank payment keys
PROBLEM
💀 There could be undetected APT malware within financial networks.
Known malware can be detected in some way, but what about the unknown ones?👮 Question: Can we detect and stop unknown/undetected malware once activated?
Conventional Approach 1 - Cybersecurity
Fighting malware with cybersecurity products
🚫 Relying on the manufacturer to prepare a malware signature.
🚫 Even if a signature is available, new variants of malware can emerge quickly.
🚫 Defining these signatures for multiple products is exhausting.
🚫 Cybersecurity products have limited support for financial protocols.
Conventional Approach 2 - Log Analysis
Collecting logs and trying to catch anomalies through analysis
🚫 Looking at network traffic and trying to relate logs from as many servers as possible to see the big picture.
🚫 Since malware exploits system vulnerabilities, it may not always generate logs.
❔🚫 Network traffic analysis is essential, but it can’t detect malware operating locally.
🚫 Collecting logs from both financial application servers and cybersecurity systems:
🌋 Performance loss and delays in log transfer may occur.
Conventional Approach 3 - Using Financial Fraud Engine
Attempting to detect malware during online transactions by integrating with financial applications’ messaging.
🚫 It’s impossible to detect malware using the limited information conveyed by the financial system.
🚫 Integrating the fraud component with other cybersecurity components is highly challenging.
Conventional Approach 3 - Using Financial Fraud Engine (ATM)
🌋 While it is possible to monitor message traffic from the ATM network in real time, matching ATM messages with approval messages from servers is required.
🌋 If the ATM dispenses cash without such an approval, an alarm should be generated.
🌋 To do this with traditional methods, logging must be enabled on all servers. This leads to slowdowns and log increases.
The conventional approach will struggle significantly.
🤔 Alternative?
Proposal: A different perspective
Airport 360-degree passenger security analogy
- Controls are in place at each step in an airport: parking lot, entrance gate, ticketing, security gate, passport control, and boarding.
- Skipping any step or detail should not be possible.
- A system is established to monitor and match each stage.
- All steps are recorded and controlled.
360-Degree Approach
360-degree perspective applied:
✅ Monitoring all components simultaneously in real-time without performance loss.
✅ Scenario sets prepared by looking at the big picture.
🌠 Bonus: Detection of anomalies in all flows using machine learning and AI algorithms.
✅ Analyzing financial protocols and catching anomalies at the financial layer.
✅ Collecting data without performance loss.
360-Degree Financial System Protection - 1
- Tracking activities in POS, ATM, internet, mobile, switch, authorization, and integration protocols.
- Monitoring and control at every stage.
- Manual scenario and rule sets can be defined.
- Machine learning and AI engine are used.
- Data collection requires no integration, taken directly from the network infrastructure.
360-Degree Financial System Protection - 2
-
Records are collected by decrypting the data passing through the wire.
-
No additional load on servers and systems during collection, hence network performance remains unaffected.
-
Technically, the port mirroring feature of network devices is utilized. Traffic from each stage is mirrored to the analysis server.
-
Captured transactions are either flagged for monitoring or blocked with the FINANCIAL TRANSACTION GATEWAY.
Conclusion
With a single solution, monitoring the financial network end-to-end and conducting compliance checks for each transaction based on rule-based and AI-based controls.
Thus, protecting against threats like unauthorized cash withdrawals from ATMs by undetected malware.
Take Action!
You can protect your financial infrastructures against complex threats like APT by using INETCO products.
Contact us for more information
Start a WhatsApp chat here
See other contact options here



